Many men and women of all ages, starting with children and teenagers, come to the doctor with itching. Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis is the most common of these skin diseases. It can happen at any age, but children are a little more likely to get eczema.
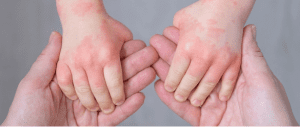
Certain skin diseases can occur during pregnancy. However, pregnancy is not a condition for eczema. Eczema is usually a disease similar to allergy or asthma that can be hereditary. Today we will discuss what eczema is, why it happens, and what to do about it. Let’s find it…
What is Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis or eczema is a type of skin inflammation. Any inflammation of the epidermis in the upper layer of the skin is commonly known as eczema or Atopic Dermatitis. Where the skin becomes reddish, itchy, grow like small grains, and sometimes water comes out from those, later black spots were also seen there.
Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis occurs first in a specific area. The skin turns reddish and then swells a little. Later small grains and blisters come out. The blisters rupture and the juice drips or pus appears due to a bacterial infection. Sometimes the small lumps merge and make the skin thick and hard.
Also Read – Peptic or Stomach Ulcer Treatment, Symptoms and Home Remedies
This is called lichenification. When lichenification is prolonged, the skin becomes very thick and stiff, and when there is less moisture in the air, the skin ruptures, forming large scabs. Then there is a feeling of intense itching, itching, tearing of the skin, and bleeding. This is Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis.
What are The Types of Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis?
Eczema can be of two types, internal eczema, and external eczema. Internal eczema is more common.
These Are The Most Common Type of Eczema:
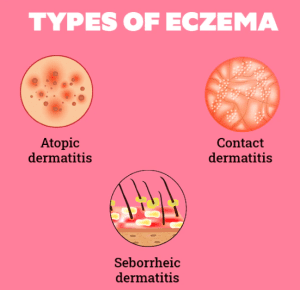
Atopic eczema Or Dermatitis:
Atopic dermatitis is the most common type of eczema. This eczema condition usually occurs in childhood and often improves with growth or after puberty.
Atopic dermatitis causes itchy, dry, and cracked skin. This skin inflammation usually appears on the hands, feet, ankles, and hands, neck, upper chest, eyebrows, inner elbows, and knees. When scratched, the skin becomes blistered and swollen. It can often be considered as most Indonesian dry eczema.
People with a history of allergies are at higher risk of developing atopic eczema, such as people with food allergies or asthma. Allergies are a major cause of eczema in young children. There are also several triggers that are known to cause atopic eczema such as soap, detergent, stress, low humidity, seasonal allergies, and cold weather.
Also Read – High Blood Pressure or Hypertension: 8 Ways To Control High Blood Pressure
Allergic Contact Eczema:
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin experiences an allergic reaction, itching, and irritation after contact with a foreign substance. Common causes of dermatitis in contact with allergens include gold/nickel or other metallic materials, perfumes, latex gloves, cosmetic ingredients, poison ivy, or poison ivy.
In dermatitis in contact with allergens, skin rashes appear in the area touched by the substance within 24 to 48 hours. The main symptoms are dry skin, redness, and blisters, swelling of the eyes. Presumably, this eczema can also be called dry eczema.
Inflammatory Contact Eczema:
Skin irritation with skin irritants such as acid ingredients, bleach, clear liquids, kerosene, and detergents actually causes irritating contact dermatitis. This type of eczema often attacks industrial workers, especially those working in the mining industry, natural resources, manufacturing, and medical services.
The most common symptom of irritating contact dermatitis is skin that feels sore, hot, and itchy. Irritating contact dermatitis often appears as dry skin or cracked skin, which is why many people refer to this as dry eczema. In some cases, itchy contact dermatitis can cause blisters that can rupture the crust of the open cause so it is often known as wet eczema.
Digidriotic Eczema:
Dyshidrotic eczema or dyshidrosis is an inflammatory condition of the skin characterized by the presence of small, fluid-filled nodules on the skin of the hands and / or the soles of the feet and between the toes.
This blister may appear for about 3 weeks and may last. These fluid-filled nodules are often mistaken for wet eczema. When the blister dries, the skin will become sore. If you scratch the area, you will find the skin to be thicker and more elastic. This is called dry eczema.
This condition is more common in women than in men. Eczema dyshidrosis is caused by chromium (usually found in salt), allergies, wet hands/feet, and stress.
Also Read – Dengue Fever: Sign & Symptoms, Prevention and Treatment of Dengue Fever
Neurodermatitis:
Neurodermatitis Atopic dermatitis is similar to eczema. This condition causes thick, scaly patches on your skin. Eczema is most commonly experienced in people who have other types of eczema or psoriasis. The cause of neurodermatitis is still unknown, although some physicians suspect that stress may be a factor.
Pneumular Eczema:
Pneumular type eczema usually causes round blisters on the body. In Latin, numbers also mean currency. Pneumular eczema can be caused by an insect bite reaction or by an allergic infection with metals and chemicals. Dry skin can also cause eczema.
Static Eczema:
This Eczema is a static type of eczema that occurs when fluid comes out of a vein into your skin. It is usually caused by a rupture of blood vessels (varicose veins). This leaking fluid can cause swelling, redness, itching, and pain in the skin. Most Indonesians calling it wet eczema.
What Causes Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis?
The exact cause of eczema could not be determined yet. Moisture protects the skin from bacteria and substances that cause allergies. The following factors are commonly the cause of Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis.
- Usually dry or rough skin is responsible for eczema because this type of skin cannot resist bacteria.
- The disease can be transmitted through various chemicals, detergents, soaps or shampoos.
- It can be transmitted from allergens such as pollen, dust, wool, wool, etc.
- Any genetic changes can lead to skin infections and infection.
- If the body’s immune system is weakened due to long-term disease, it can lead to bereavement.
- It can be caused by closing the sweat glands due to various bacteria.
- Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis can also be caused by environmental factors. Such as- excessively hot or excessively cold or damp wet weather, etc.
- Again, any hormonal changes, especially in women, Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis can occur during menstruation or pregnancy.
Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis Sign and Symptoms:
Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis includes dry or rough skin, reddened skin, inflamed skin, or itchy skin. There may be small watery rashes on the skin of the hands and feet. If the skin is infected again, the skin may become wet and pus may come out. Frequent itching of the skin can cause thickening.
Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis Diagnosis:
Eczema can be diagnosed by looking at the eyes. A dermatologist examines the skin at the clinic to see if you have eczema. Red, dry, and itchy skin is a feature of this disease. If your child has persistent fever and other accompanying symptoms, the doctor will advise you to have an initial blood test. Sometimes some laboratory tests can be done and in some exceptional cases, the skin may need to be cut and sent for histopathological examination.
Who is at Risk of Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis?
- If one member of the family has eczema or Atopic Dermatitis, the chances of having eczema to other members also increase.
- If the skin is dry or rough, the chances of getting eczema are high because such skin cannot resist bacteria.
- The use of various chemicals, detergents, soaps, or shampoos also increases the risk of infection.
- Eczema can be caused by exposure to allergens such as pollen, dust, wool, etc.
- Genetic changes can increase the risk of eczema if the skin’s immune system is weakened.
- A person who is engaged in the care of a patient suffering from skin disease is more likely to get this disease.
- Children living in urban areas have a higher risk of contracting the disease, especially children in daycare or child care.
- Excessive heat or excessively cold or damp wet weather can also cause eczema.
- Any hormonal changes, especially in women, can cause eczema during menstruation or pregnancy.
- The risk of eczema increases when the body’s immune system is weakened due to long-term disease.
- It can be caused by various bacterial infections by closing the sweat glands.
How to Prevent Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis?
- Items that exacerbate binge eating or eczema or foods that increase it should be avoided.
- Always wear soft and comfortable clothes. Synthetic or woolen clothing should not be worn if you have allergies.
- Don’t use artificial colors and unscented soaps or detergents to clean clothes.
- Stay away from dust, flower pollen, and cigarette smoke which can cause allergies.
- The affected area cannot be scratched.
- Must be free from excessive anxiety and stress.
- Instead of leaving the skin dry, use artificial colors and unscented lotions or creams if necessary.
Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis Treatment:
Treatment is not too difficult. Before we start please note that we are not telling you to take medicines by yourself without consulting with a doctor, always consult with your doctor before taking any medicine.
Potassium permanganate granules can be mixed with lukewarm water and washed once or twice a day. Steroid mixed antibiotic ointment or cream should be applied twice daily for seven to 14 days, may require more days if it’s needed. Sometimes it can be used with anti-fungal cream if there any fungal infection with eczema.
In adult patients, Fexofenadine tablets 120 mg twice daily should be administered orally for several weeks. In the case of children, the dose will be much lower, which actually depends on the age and weight of the child.
If there are enough bacterial infections, then you may have to take antibiotic capsules or tablets for a week. Sometimes eczema can be accompanied by a lack of vitamins. In that case, vitamin tablets, especially vitamin B complex, can be taken twice a day for 15 days to a month.
Steroids in Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis:
Steroid medications should never be taken unless the eczema is very severe and without a doctor’s advice. Steroid-like drugs have many side effects that can be serious, especially oral steroids. So eczema patients should try to avoid such drugs. However, there is no problem to apply steroid ointment cream or lotion on the skin. Because it enters in the body very little. Low energy steroid creams can be applied to young children.
Is Eczema Gets cured?
With proper treatment and avoidance of the cause of eczema, external eczema is eliminated in almost all cases. Internal eczema also heals in most cases, but, its treatment is a little chronic. Internal eczema tends to back again.
Is eczema hereditary?
Some eczema, such as atopic eczema and lichen simplex is hereditary. However, if parents had or have eczema, there is no confirmation that all the children will get this disease. There is usually no hereditary relationship with contact eczema, scabies eczema, or fungal eczema.
Final Words:
A permanent cure for some internal eczema has not been discovered yet. It is possible to prevent itching or its spread by taking care of yourself and taking treatment if necessary. For example, salty soaps and other chemicals should be avoided, only necessary creams should be used, the skin should not be kept dry, comfortable and soft cloths should be used, skincare should be taken to prevent skin diseases, etc. Eczema can be accompanied by asthma and allergic rhinitis. If you have atopic dermatitis or eczema and it causes long term problems, you must consult a doctor.